Digital Social Responsibility: A Path to a More Ethical Digital Society
In an era where the digital realm pervades almost every aspect of our lives, the concept of digital social responsibility (DSR) has emerged as an imperative. DSR encompasses the ethical, responsible, and sustainable use of digital technologies and platforms by individuals, organizations, and governments.
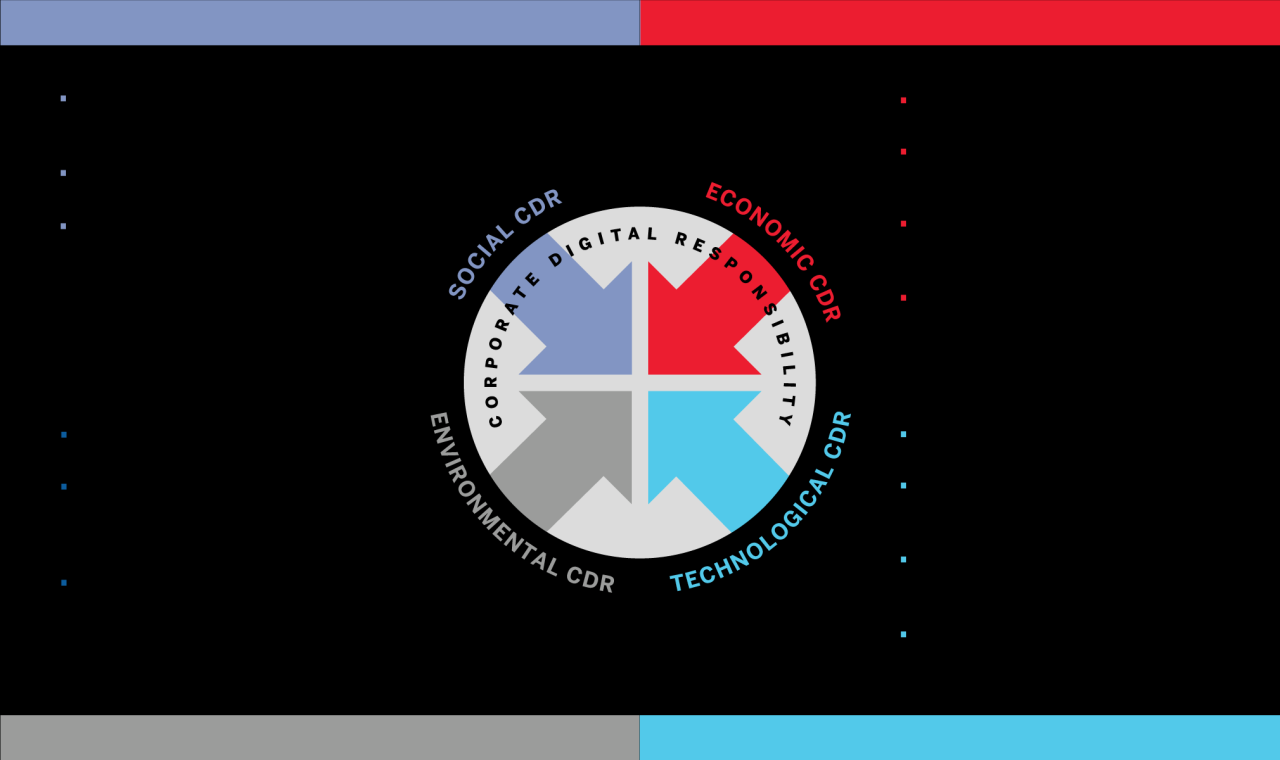
Pillars of Digital Social Responsibility
DSR rests upon several key pillars:
- Privacy and Data Protection: Ensuring the privacy of individuals and protecting their personal data from misuse.
- Digital Literacy and Inclusion: Promoting digital skills and access to empower all individuals to participate fully in the digital economy.
- Cybersecurity and Safety: Safeguarding digital systems and infrastructure from cyberattacks and other threats.
- Accountability and Transparency: Holding individuals and organizations accountable for their actions in the digital space.
- Environmental Sustainability: Minimizing the environmental impact of digital devices and practices.
Benefits of Digital Social Responsibility
Implementing DSR practices brings numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Trust and Confidence: Promotes trust among individuals, businesses, and the government by ensuring ethical and responsible use of technology.
- Empowerment and Inclusion: Fosters digital literacy and inclusion, creating opportunities for all to participate in the digital economy.
- Improved Safety and Security: Reduces the risk of cyberattacks and other digital threats, protecting individuals and businesses.
- Positive Social Impact: Leverages digital technologies for social good, addressing issues such as poverty, education, and healthcare.
- Environmental Responsibility: Promotes sustainable practices that reduce the carbon footprint of the digital realm.
Implementation of Digital Social Responsibility
DSR can be implemented through various initiatives:
- Government Regulations: Establishing laws and policies that protect individuals’ privacy, promote cybersecurity, and address other DSR issues.
- Industry Standards: Developing industry-wide standards and best practices for responsible digital behavior.
- Corporate Policies: Implementing corporate policies that prioritize DSR principles, ensuring ethical and responsible use of technology within organizations.
- Individual Responsibilities: Encouraging individuals to use digital technologies responsibly, safeguarding their privacy, and promoting digital literacy.
- Educational Initiatives: Incorporating DSR concepts into education curricula, fostering a culture of responsible digital citizenship.
Challenges and Opportunities
While DSR holds immense promise, it also faces challenges:
- Complexity: The rapid pace of technological advancements makes it difficult to keep up with the evolving DSR landscape.
- Global Reach: DSR issues are often transnational, requiring international cooperation and harmonized policies.
- Balancing Interests: Balancing the need for regulation and privacy protection with the benefits of innovation and economic growth.
Despite these challenges, DSR presents significant opportunities to create a more ethical, responsible, and inclusive digital society. By embracing DSR principles, we can harness the power of technology for good while mitigating its potential risks.
Conclusion
Digital social responsibility is an essential component of a responsible and sustainable digital future. By prioritizing privacy, digital literacy, cybersecurity, accountability, and environmental sustainability, we can foster a digital society that empowers individuals, protects our data, and promotes social progress. Implementing DSR practices is an ongoing journey that requires collaboration and commitment from all stakeholders, creating a more ethical and responsible digital realm that benefits all.