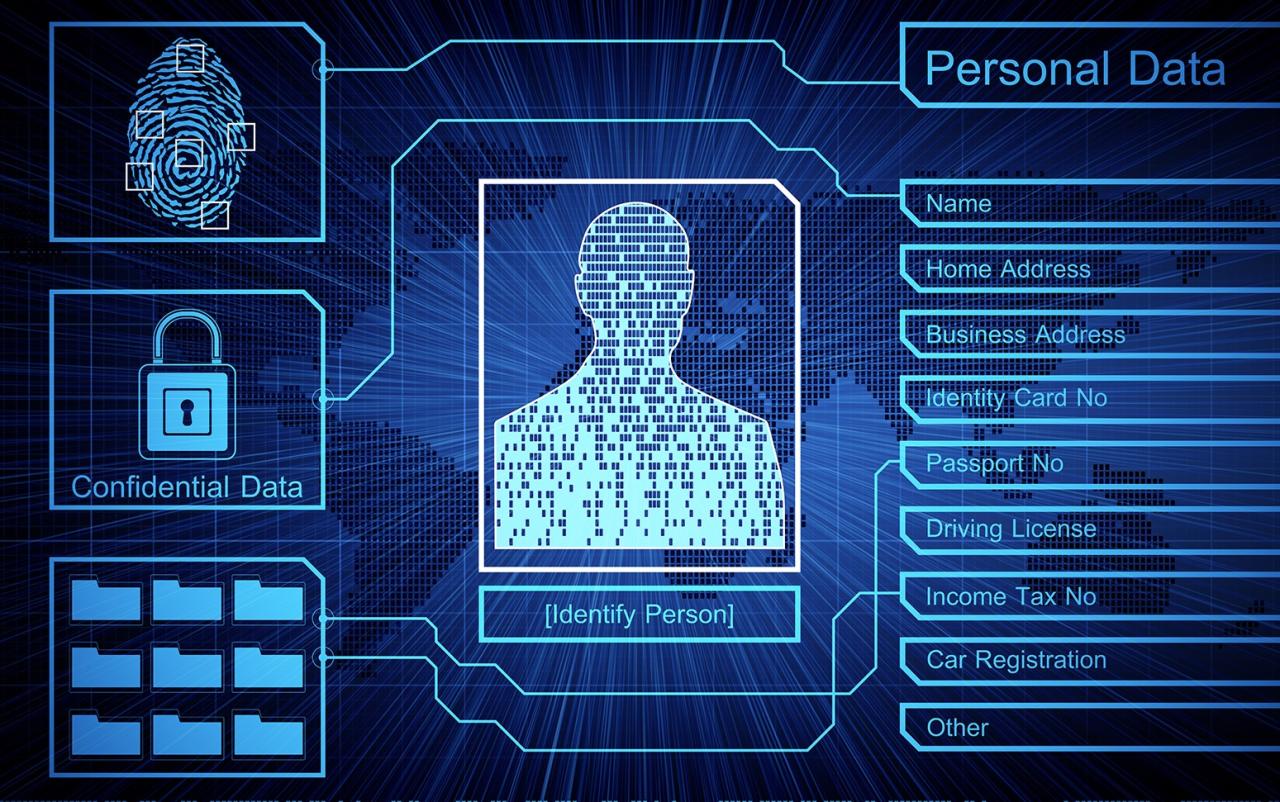
Personal Data Security
Personal data refers to any information that can be used to identify, locate, or contact an individual. This includes sensitive information such as social security numbers, financial account details, and health records.
Importance of Personal Data Security
Protecting personal data is crucial for several reasons:
- Identity Theft: Personal data can be used by criminals to assume your identity, open fraudulent accounts, or make unauthorized purchases.
- Financial Fraud: Financial information can be stolen to access bank accounts, make unauthorized withdrawals, or apply for loans in your name.
- Medical Identity Theft: Health records can be used to obtain medical services, prescriptions, or insurance coverage without your knowledge.
- Privacy: Personal data can be used to track your movements, monitor your online activity, or target you with personalized advertisements.
Threats to Personal Data Security
Various threats can compromise personal data security, including:
- Data Breaches: Data breaches occur when unauthorized parties gain access to sensitive data stored by companies or institutions.
- Malware: Malware, such as viruses, spyware, and ransomware, can infect devices and steal personal information.
- Phishing Scams: Phishing scams attempt to trick individuals into revealing personal data by posing as legitimate organizations.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineers manipulate individuals into providing personal information or granting access to sensitive systems.
- Insider Threats: Employees with access to sensitive data can intentionally or unintentionally compromise its security.
Best Practices for Personal Data Security
To protect your personal data, consider the following best practices:
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex, unique passwords for all online accounts and change them regularly.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication: Enable multi-factor authentication to require additional verification beyond a password, such as a code sent to your phone.
- Be Cautious of Public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing sensitive information on public Wi-Fi networks, as they may be vulnerable to eavesdropping.
- Limit Social Media Sharing: Only share necessary personal information on social media and be aware of privacy settings to control who can access your posts.
- Be Aware of Phishing Scams: Carefully scrutinize emails, text messages, and other communications from unknown senders claiming to be from legitimate organizations. Never click on suspicious links or provide personal information.
- Use a VPN for Privacy: Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your data from eavesdropping.
- Monitor Your Credit Reports: Regularly review your credit reports for unauthorized activity and report any suspicious transactions immediately.
- Freeze Your Credit: Consider freezing your credit to prevent unauthorized access to your financial accounts.
- Educate Yourself about Data Privacy: Stay informed about data privacy laws and best practices to protect your personal information.
Conclusion
Personal data security is essential to safeguard your identity, finances, privacy, and health. By following these best practices, you can minimize the risks associated with data breaches and protect your personal information from falling into the wrong hands. Remember, it is your responsibility to protect your data, and vigilance is key to maintaining its security.