Virtual Reality (VR)
Introduction
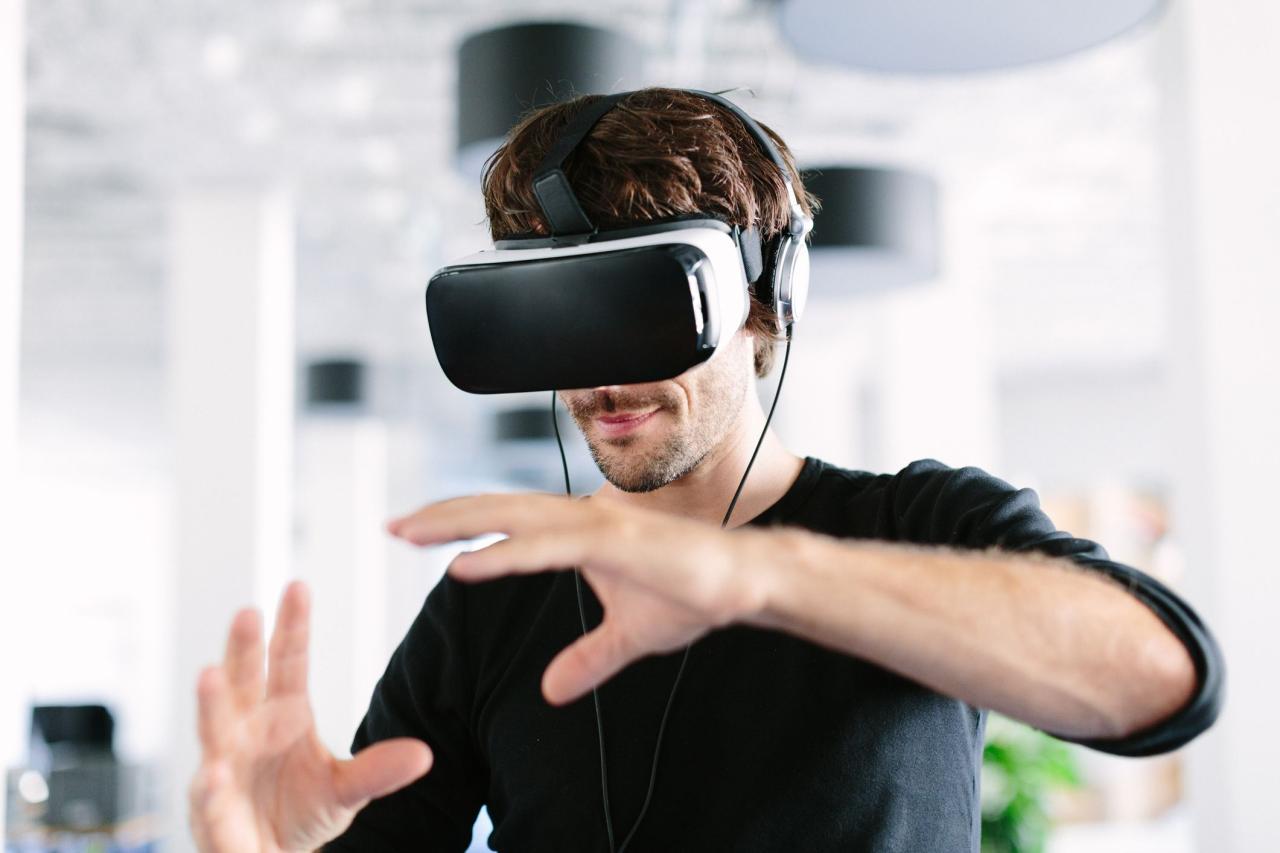
Virtual reality (VR) is a simulated environment that can be created with computer technology. VR headsets are worn over the eyes, blocking out the real world and replacing it with a virtual one. This allows users to experience immersive and interactive environments that can be used for entertainment, education, and training.
How VR Works
VR headsets use two high-resolution displays, one for each eye. These displays create a stereoscopic effect, making the virtual environment appear three-dimensional. The headsets also track the user’s head and hand movements, allowing them to interact with the virtual environment.
Types of VR Headsets
There are several types of VR headsets available, including:
- Tethered headsets: These headsets are connected to a computer via a cable, providing high-quality graphics and low latency.
- Stand-alone headsets: These headsets do not require a computer, as they have their own built-in hardware. They offer more freedom of movement but may have lower graphics quality.
- Mobile VR headsets: These headsets use a smartphone as their display. They are affordable and portable but offer a less immersive experience.
Applications of VR
VR has numerous applications across various industries:
Entertainment: VR games and experiences provide immersive and engaging gameplay. It also allows for the creation of interactive virtual worlds for social interactions.
Education: VR can be used for virtual field trips, simulations, and hands-on learning experiences. It provides students with access to realistic and immersive environments that enhance their understanding.
Training: VR can be used to train employees in a safe and controlled environment. It allows for realistic simulations of dangerous or complex situations, reducing the risk of accidents.
Healthcare: VR can be used for pain management, phobias, and rehabilitation. It provides patients with a distraction-free environment that can alleviate stress and anxiety.
Other Applications: VR has also found applications in architecture, design, engineering, and tourism, enabling users to visualize and interact with virtual environments before they are built or experienced.
Benefits of VR
- Immersive and engaging experiences: VR provides a highly immersive and engaging experience that can transport users to different worlds or situations.
- Interactivity: VR allows users to interact with the virtual environment, making it more realistic and engaging.
- Educational value: VR can be used for educational purposes, providing students with access to immersive learning experiences.
- Training applications: VR can be used to train employees in a safe and controlled environment, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Therapeutic benefits: VR can have therapeutic benefits for pain management, phobias, and rehabilitation.
Challenges of VR
- Motion sickness: Some users may experience motion sickness while using VR headsets.
- Eye strain: Prolonged use of VR headsets can lead to eye strain.
- Cost: High-quality VR headsets can be expensive.
- Technical limitations: VR technology is still in development, and there are limitations in graphics quality, latency, and field of view.
Future of VR
VR is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing advancements in hardware, software, and applications. As technology improves, VR is expected to become even more immersive, affordable, and accessible. The future of VR holds the potential for transformative experiences across various industries and aspects of life.