Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA) – The Future of Data Security in a Remote Work Era
Introduction
The advent of remote work has revolutionized work dynamics, but it has also exposed organizations to new data security risks. Traditional security models, heavily reliant on perimeters and implicit trust, are no longer sufficient in the decentralized environments of today. Enter Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA), a paradigm shift in data protection that is gaining traction as the preferred solution for organizations embracing remote work.
What is Zero-Trust Architecture?
ZTA is a security framework based on the principle of "never trust, always verify." It assumes that no user, device, or network is inherently trustworthy and requires continuous authentication and authorization for access to resources. By eliminating implicit trust and enforcing strict access controls, ZTA minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
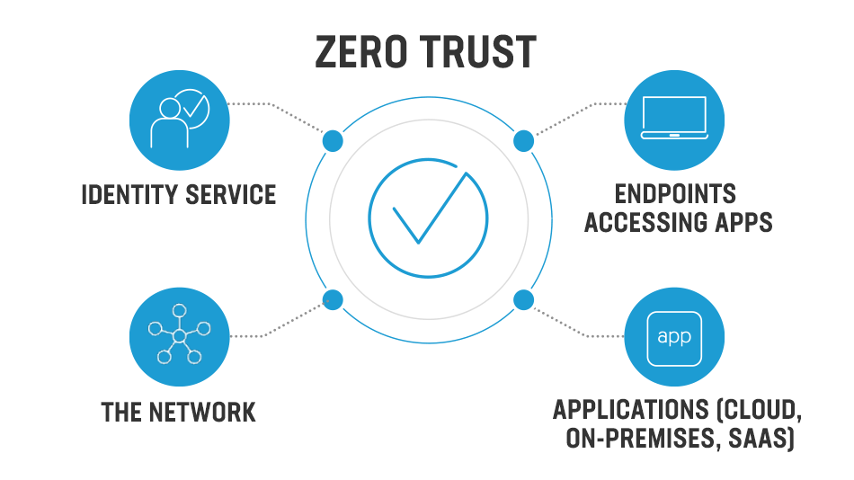
Components of ZTA
ZTA comprises several key components:
- Identity Management: Centralized management and authentication of users and devices.
- Policy Enforcement: Enforcement of access policies and authorization based on user identity, device, and context.
- Device Security: Robust endpoint security measures to protect devices from vulnerabilities and intrusion.
- Network Isolation: Segmentation of the network into smaller, isolated segments to minimize the impact of breaches.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and analysis of system and user behavior to detect and respond to potential threats.
Benefits of ZTA
ZTA offers numerous benefits for organizations, including:
- Enhanced Data Security: Reduced risk of data breaches and unauthorized access by eliminating implicit trust.
- Improved Compliance: Alignment with regulatory frameworks and industry best practices for data protection.
- Increased Agility: Reduced reliance on static network infrastructure, enabling organizations to adapt to remote work models and cloud-based services.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automated authentication and access control processes reduce administrative overhead and operational costs.
Key Considerations for ZTA Implementation
Implementing ZTA requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should consider the following:
- Phased Deployment: Break down the implementation into manageable stages to minimize disruption.
- User Adoption: Ensure users understand and embrace the new authentication and access protocols.
- Vendor Selection: Evaluate vendor solutions that align with the organization’s specific requirements.
- Regular Review and Updates: Continuously monitor and update ZTA policies and configurations to address evolving security threats.
Conclusion
Zero-Trust Architecture is the cornerstone of modern data security in the era of remote work. By eliminating implicit trust and enforcing strict access controls, ZTA significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Organizations looking to protect their data and maintain compliance should prioritize the implementation of a comprehensive ZTA strategy.



