Cloud Security: Safeguarding Cloud-Based Infrastructures in the Era of Cloud Migration
Introduction
The rapid adoption of cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations store, process, and access data. As more and more businesses entrust their sensitive information to cloud-based platforms, securing these infrastructures has become paramount. Cloud security refers to the comprehensive set of measures implemented to protect cloud assets, data, services, and applications from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Importance of Cloud Security
The importance of cloud security cannot be overstated. Inadequate security measures can expose organizations to a multitude of risks, including:
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to cloud-based data can result in the theft, misuse, or destruction of sensitive information.
- Service disruptions: Cyberattacks can disrupt cloud services, leading to business downtime and financial losses.
- Compliance violations: Failure to comply with industry regulations and standards can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
- Reputational damage: Security breaches can erode public trust and damage an organization’s reputation.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
To mitigate the risks associated with cloud computing, organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to cloud security. Best practices include:
- Shared Responsibility Model: Organizations should understand that cloud providers are responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure itself, while organizations retain responsibility for the security of their data and applications in the cloud.
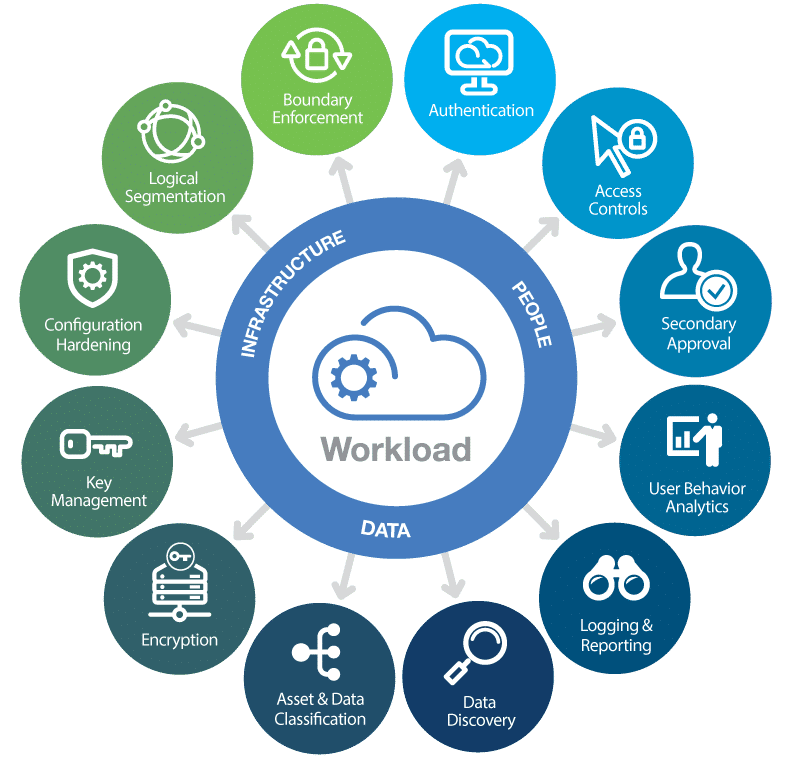
- Data Encryption: Encryption is crucial for protecting data both at rest and in transit. Organizations should leverage encryption mechanisms provided by cloud providers and implement additional encryption layers when necessary.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication mechanisms to add an additional layer of security to cloud access.
- Access Control: Establish granular access controls to restrict who can access specific cloud assets and data.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Implement continuous monitoring and alerting mechanisms to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real time.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with best practices.
Cloud-Specific Security Controls
In addition to general security measures, cloud platforms offer a range of cloud-specific security controls to enhance protection. These controls include:
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): VPCs provide private and isolated networking environments within a cloud provider’s infrastructure.
- Security Groups: Firewalls that control incoming and outgoing traffic to specific cloud resources.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): A security gateway that monitors and controls access to cloud services from both inside and outside the organization.
- Identity and Access Management: Cloud platforms offer identity management services to manage user identities, permissions, and access policies.
Conclusion
Cloud security is a critical aspect of cloud computing. By implementing a comprehensive approach to security, organizations can mitigate risks, protect their sensitive data, and ensure the reliability and integrity of their cloud-based infrastructures. Adopting best practices, leveraging cloud-specific security controls, and fostering collaboration between cloud providers and organizations is essential to achieve a secure cloud environment.



