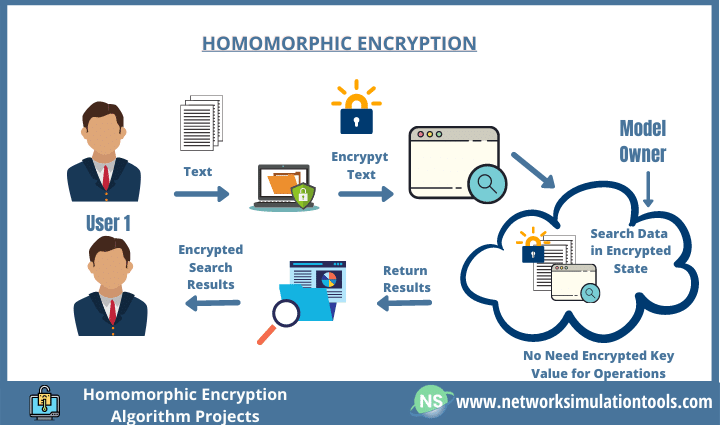
Homomorphic Encryption: Empowering Data Analysis While Preserving Privacy
Introduction
Data analysis has become an indispensable aspect of modern society, aiding us in understanding complex patterns, making informed decisions, and driving innovation. However, traditional data analysis methods often require data to be decrypted before processing, which poses privacy concerns when dealing with sensitive or confidential information.
Enter Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption is an advanced encryption technique that allows data to be processed while it remains encrypted. This enables data analysis to be performed on encrypted data without the need for decryption, ensuring the privacy of the underlying information.
How Homomorphic Encryption Works
Homomorphic encryption relies on mathematical operations called homomorphisms, which allow operations to be performed on encrypted data and produce encrypted results that correspond to the operations performed on the plaintext data.
Specifically, homomorphic encryption schemes have two key properties:
- Add homomorphism: Allows addition and subtraction operations to be performed on encrypted data, resulting in encrypted outputs that correspond to the sum or difference of the plaintext values.
- Multiplication homomorphism: Allows multiplication operations to be performed on encrypted data, resulting in encrypted outputs that correspond to the product of the plaintext values.
Benefits of Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption offers significant benefits for privacy-preserving data analysis:
- Enhanced Privacy: Data remains encrypted throughout the analysis process, eliminating the risk of sensitive information being exposed.
- Secure Collaboration: Multiple parties can collaborate on data analysis without revealing their respective data to each other.
- Improved Data Security: Encrypted data is protected against unauthorized access, ensuring that it remains secure even in the event of a breach.
Applications of Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption has a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
- Healthcare: Analyzing encrypted medical records without compromising patient privacy.
- Finance: Performing financial computations on encrypted financial data to enhance data security and prevent fraud.
- Cloud Computing: Enabling secure data analysis on cloud platforms without requiring data decryption.
Current Challenges and Future Prospects
While homomorphic encryption offers immense potential, it still faces some challenges:
- Computational Complexity: Homomorphic encryption algorithms are computationally expensive, making real-time data analysis impractical in some cases.
- Key Management: Managing and distributing homomorphic encryption keys securely is crucial to ensure the integrity and security of the encrypted data.
Researchers are actively working on addressing these challenges and improving the performance and usability of homomorphic encryption. As these advancements continue, the adoption of homomorphic encryption in various applications is expected to grow significantly.
Conclusion
Homomorphic encryption revolutionizes data analysis by allowing it to be performed on encrypted data, safeguarding privacy and enhancing data security. With its benefits and growing potential, homomorphic encryption is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of data analysis in various industries.