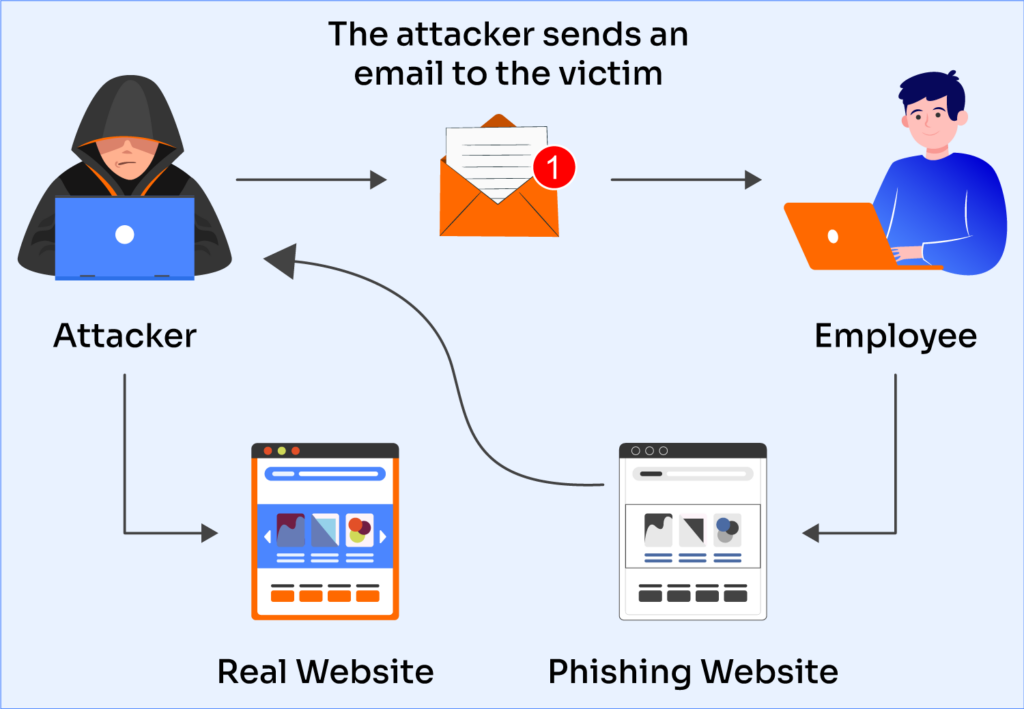
Phishing Prevention: Essential Strategies to Protect Your Organization
Introduction:
Phishing continues to be a prevalent threat in the cybersecurity landscape, targeting individuals and organizations with sophisticated attacks. This type of social engineering aims to trick victims into disclosing sensitive information, such as credentials or financial data. Therefore, implementing robust phishing prevention strategies is crucial to safeguard your organization from potential breaches.
Understanding Phishing Types:
Before exploring prevention strategies, it’s essential to understand the various phishing techniques employed by attackers:
- Email Phishing: Fraudulent emails that mimic legitimate sources, tricking recipients into clicking malicious links or downloading attachments.
- Spear Phishing: Targeted attacks that use personalized emails to impersonate known contacts or organizations, increasing the likelihood of success.
- Smishing: Phishing attempts via SMS messages, often containing links to phishing websites or requesting personal information.
- Vishing: Voice-based phishing calls that attempt to deceive victims into divulging confidential data.
Preventive Measures:
1. Employee Education and Awareness:
Educating employees about phishing techniques and how to identify suspicious emails and messages is vital. This includes recognizing common phishing red flags, such as unfamiliar sender addresses, misspellings, and urgent calls to action.
2. Email Filtering and Anti-Spam Solutions:
Deploying email filtering and anti-spam tools can automatically detect and block phishing emails based on known patterns and suspicious characteristics.
3. Email Authentication Protocols:
Implement email authentication protocols like DKIM, SPF, and DMARC to verify the authenticity of emails and prevent spoofing attempts.
4. Anti-Phishing Software:
Invest in anti-phishing software that scans inbound communications and identifies suspicious links, attachments, and other indicators of phishing attacks.
5. Web Browser Extensions:
Install web browser extensions that provide real-time protection against phishing websites. These extensions often include phishing URL detection, warning users before they visit malicious sites.
6. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Enable 2FA for critical accounts to add an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide a secondary form of authentication in addition to their password.
7. Secure Web Browsing Practices:
Encourage safe web browsing practices, such as avoiding clicking on unknown links or downloading attachments from dubious sources.
8. Regular Security Updates:
Ensure that all software, operating systems, and applications are regularly updated with the latest security patches to address emerging phishing threats.
9. Incident Response Plan:
Establish a clear incident response plan outlining the steps to take in the event of a phishing attack. This plan should include communication protocols, containment measures, and remediation actions.
10. Third-Party Risk Management:
Evaluate the phishing prevention measures of third-party vendors that have access to your organization’s data and systems. Ensure they adhere to industry best practices to minimize potential exposures.
Conclusion:
Phishing prevention requires a multi-layered approach that combines employee education, technological solutions, and organizational policies. By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Remember, staying vigilant and continuously adapting to evolving phishing tactics is essential for maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture.